Consultation services based on conventional procurement methods
Energy Audit
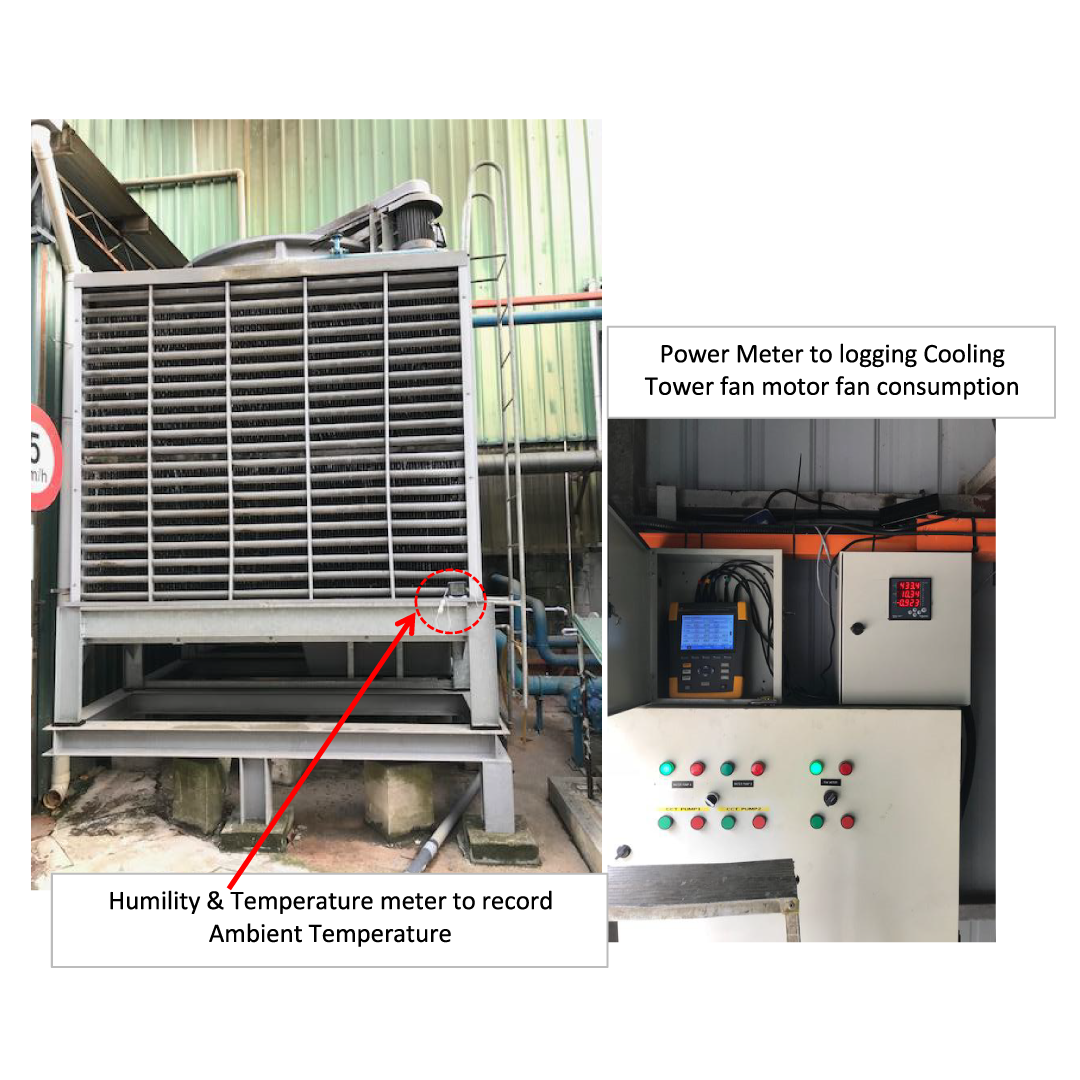
An energy audit is a systematic assessment of the baseline energy consumption efficiency within a facility, followed by identification of energy efficiency improvement opportunities and cost-saving measures. Depending on the type of premise and equipment involved, an energy audit scope may include electrical and thermal energy. An energy audit may be conducted on a whole premise, on a selected, high energy consuming area, or on a specific equipment/system.
An energy audit is conducted to achieve key goals: –
- To assess the energy utilization performance of a facility, its processes and equipment/system,
- To reduce energy losses and improve the facility’s energy efficiency, and
- To reduce the energy bills and improve the profit margin of the affected organization.
We highly recommend that the installation periodically conduct a continuing energy audit to sustain an efficient operation, avoid energy and cost wastage, and stay competitive. The findings and recommendations from the energy audits can be used as a basis for a company to implement a sustainable energy management improvement program. The required regular reporting of such energy management program can, in turn, help the company abide by the Energy Commission requirement to submit energy consumption report every six months.

Energy Planning Process

Energy Planning Process Concept Diagram
There are three types of Energy Audit.
i. Preliminary Energy Audit
Preliminary Energy Audit (PEA) or ‘walk-through audit’ provides an overview of a facility’s current energy scenario. During PEA, auditors usually identify energy losses through visual observations, apply energy conservation rules-of-thumb, and make quick estimates of potential energy and cost-saving measures. The study may result in a quick recommendation of no-cost and low-cost measures.
ii. Detailed Energy Audit
Detailed Energy Audit (DEA) involves a thorough energy balance analysis and evaluation to establish the baseline energy consumption within a facility. DEA typically involves measurement of parameters influencing energy consumption, identifying areas of significant energy users, generating the energy distribution profile of a facility, energy trend analysis, area and equipment energy efficiency analysis, and identifying energy-saving measures (ESMs) and economic analysis of the proposed energy-saving measures.
iii. Investment-grade Audit
Energy-Saving Measures (ESMs) require significant investment in capital, personnel, and other resources. The facility owner is recommended to seek expert advice to perform a more thorough cost-benefit feasibility analysis.
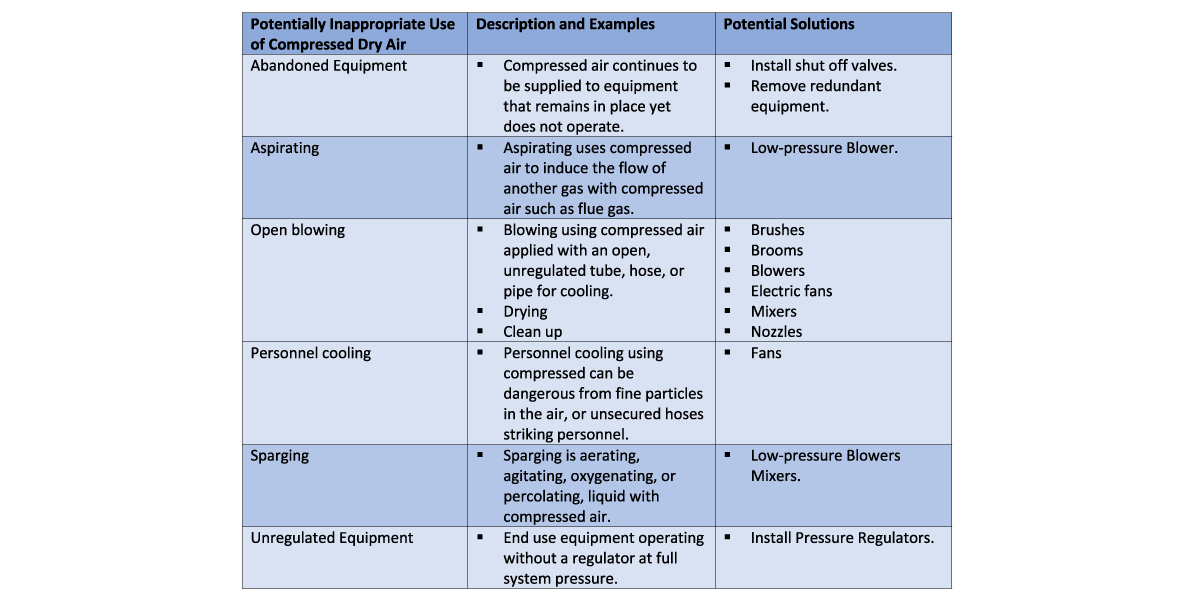
Inappropriate Use of Compressed Dry Air